An optical microscope is a microscope that typically uses visible light and a lens system to produce magnified images of small objects. While many complex designs are aimed at improving resolution and sample contrast, basic light microscopy can be very simple.
There are two basic types of light microscopes: simple microscopes and compound microscopes. Simple microscopes utilize the optical power of a single lens or lens group for magnification. Compound microscopes use a system of lenses (one set magnifies the image produced by the other) to achieve a higher magnification of objects.
What is a Compound Microscope?
A compound microscope is an instrument used to observe magnified images of small samples on glass slides. It can achieve higher magnification than stereo or other low-power microscopes, and reduce chromatic aberration.
It does this by using two or more lenses in the objective and eyepiece. The objective lens or objective lens on the nosepiece has a short focal length, close to the target sample, collects light, and focuses the image of the object into the microscope. A second lens in the eyepiece has a longer focal length to further magnify the image.
The difference between simple and compound microscopes is that simple microscopes use only one lens while compound microscopes use multiple lenses.
Schematic diagram of a compound microscope
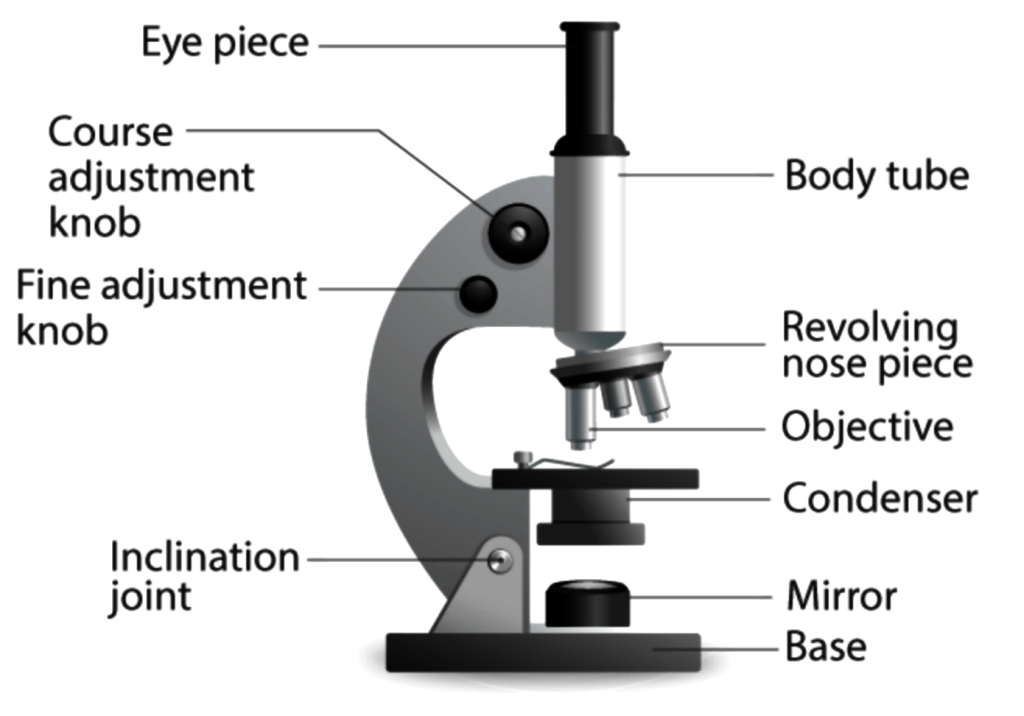
Parts and Functions of Compound Microscopes
Compound microscopes are high-power (high magnification) microscopes that use a compound lens system. Compound microscopes have multiple lenses: the objective (usually 4x, 10x, 40x, or 100x) is compounded (multiplied) with the eyepiece (usually 10x) to obtain 40x, 100x, 400x, and 1000x High magnification. Higher magnifications can be achieved by using two lenses instead of just a single magnifying lens. While eyepieces and objectives produce high magnification, a condenser below the stage focuses light directly into the sample.
How Compound Microscopes Work
A compound microscope is considered one of the standard microscopes that can be used for general purposes. The arrangement of lenses can magnify objects in complex systems.
Light begins its journey at the base of the microscope from the source of illumination. This light travels up through the condenser and aperture, and then through the contents of the stage. The image of the slide or specimen on the stage is picked up by the powerful magnification (4x, 10x or 100x) of the objective lens above it. The light then travels up the microscope head, to the eyepiece, and is again magnified by the eyepiece (5x-30x, 10x eyepieces are by far the most common).
There are two types of lenses used in compound microscopes:
- The objective lens is placed close to the object to be inspected.
- The eyepiece can observe the image.
Pass light through thin transparent objects. Obtain a magnified image of an object through an objective lens. This image is called a real image. The eyepiece then magnifies the real image even more and is seen as a virtual image. Compound microscopes are also known as brightfield microscopes because the light passes through two lenses directly through the light source to the eye. This mechanism brightens the field of view.
Compound Microscope Parts
Compound microscopes are primarily used to study structural details in slices of cells, tissues or organs. The components of a compound microscope can be divided into two parts:
- Non-optical parts
- Optical parts
Features of Compound Microscopes
- Two or more convex lenses
- Typical magnification ranges from 40x to 1000x
- Use one target at a time
- Two-dimensional image
- Monocular, binocular, trinocular, and multi-head configurations are available
Pros and Cons of Compound Microscopes
A. Advantages of Compound Microscope
- Due to the use of multiple lenses, detailed information on the sample can be obtained.
- These microscopes have their own light source.
- The microscope is user-friendly and easy to operate.
B. Disadvantages of Compound Microscopes
- Sample amplification is limited.
Uses of Compound Microscopes
- Disease identification in a pathology laboratory becomes easy with the help of a compound microscope.
- Forensic laboratories use compound microscopes to detect human fingerprints.
- The presence of metals can be detected with the aid of a compound microscope.
- With the help of a compound microscope, the study of bacteria and viruses becomes easy.
- The school uses the compound microscope for academic purposes.