Optical glass can change the direction of light propagation and change the relative spectral distribution of ultraviolet, visible, or infrared light.
Optical glass in the narrow sense refers to colorless optical glass; optical glass in the broad sense also includes colored optical glass, laser glass, quartz optical glass, anti-radiation glass, ultraviolet and infrared optical glass, fiber optic glass, acoustic glass, magneto-optical glass, and photochromic Glass.
Optical glass can be used to manufacture lenses, prisms, mirrors, and windows in optical instruments. Components made of optical glass are key elements in optical instruments.
Optical glass is the foundation and an important part of the optoelectronic technology industry.
Especially after the 1990s, with the continuous integration of optics, electronic information science, and new material science, the application of optical glass as the basic material of optoelectronics in the three major fields of optical transmission, optical storage, and optoelectronic display has advanced by leaps and bounds. Social informatization is especially one of the basic conditions for the development of optoelectronic information technology.
A brief introduction to optical glass
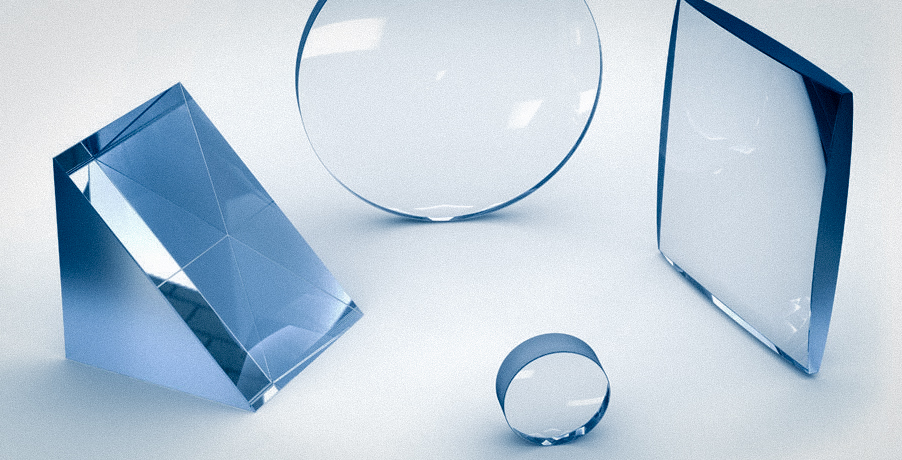
Optical glass is a glass material used to manufacture lenses, prisms, mirrors, windows, etc. of optical instruments or mechanical systems. Including optical quartz glass, colorless optical glass (usually referred to as optical glass), colored optical glass, radiation-resistant optical glass, and radiation-resistant glass, etc.
Optical glass has high transparency, high uniformity in chemistry and physics (structure and performance), and specific and precise optical constants. It can be divided into silicate, borate, phosphate, fluoride, and chalcogenide series. There are many varieties, mainly classified according to their positions in the refractive index (nD)-Abbe value (VD) diagram.
Traditionally, various types of glass with nD>1.60, VD>50 and nD<1.60, VD>55 are designated as crown (K) glass, and other types of glass are designated as flint (F) glass.
Crown glass is generally used as a convex lens, and flint glass is used as a concave lens.
Usually, the crown glass belongs to the alkali-containing borosilicate system, the light crown glass belongs to the aluminosilicate system, the heavy crown glass and barium flint glass belong to the alkali-free borosilicate system, and most of the flint glasses belong to the lead potassium silicate system. system.
With the continuous expansion of the application field of optical glass, its varieties are constantly expanding, and its composition includes almost all elements in the periodic table.
An inorganic glassy material that transmits light by refraction, reflection, or transmission, or changes the intensity or spectral distribution of light by absorption. It has stable optical properties and high optical uniformity.
Advances in Optical Glass
As technology develops, the demand for high-quality optical glass used in technology continues to increase. Its exceptional clarity and precision, combined with high chemical and temperature resistance, make optical glass an ideal material for advanced technological applications, including robotics, virtual reality displays, laser devices, and 3D printing. Market forecasts indicate an increasing demand for optical glass as developers continue to explore its use in new and improved technologies.
Classification of optical glass
1. Optical quartz glass
With silicon dioxide as the main component, it has the characteristics of high-temperature resistance, low expansion coefficient, high mechanical strength, and good chemical properties. It is used to manufacture prisms, lenses, windows, and reflectors that have special requirements for the transmission of various wavelength bands. In addition, there are photomasks, liquid crystal display panels, and disc-based thin glass used in large-scale integrated circuits; magneto-optical glass in which the polarization plane rotates when light passes through the glass along the direction of magnetic force lines; light passes through the glass in a certain direction Ultrasonic glass, acoustic glass that undergoes light diffraction, reflection, convergence, or optical frequency shift.
Special optical glass is an indispensable and important basic material in the development of the modern information industry, optics, light source, photovoltaic, semiconductor, and other national strategic and pillar emerging industries and national defense fields, and plays a key role.
2. Anti-radiation optical glass
It has a greater absorption capacity for high-energy radiation. There are high-lead glass and CaO-B2O2 system glass. The former can prevent γ-ray and X-ray radiation, and the latter can absorb slow neutrons and thermal neutrons. It is mainly used in the nuclear industry. , medical fields, etc. as shielding and peeping window materials.
3. Radiation-resistant optical glass
Under certain γ-ray and X-ray irradiation, the transmittance in the visible area changes less, and the variety and grade are the same as colorless optical glass, which is used to manufacture optical instruments and peep windows under high-energy irradiation.
4. Colored optical glass
Also known as filter glass. It has selective absorption and transmission properties for specific wavelengths in the ultraviolet, visible, and infrared regions. According to the spectral characteristics, it is divided into three types: selective absorption type, cut-off type, and neutral gray; according to the coloring mechanism, it is divided into ion coloring, metal colloid coloring, and sulfur selenium. There are three types of compound coloring, mainly used in the manufacture of optical filters.
5. Ultraviolet and infrared optical glass
It has specific optical constants and high transmittance in the ultraviolet or infrared band and is used as an ultraviolet or infrared optical instrument or as a window material.
Applications of Optical Glass
Due to its exceptional clarity and durability, optical glass is the most commonly used material in a variety of optical applications, including:
- Lenses for analytical and medical equipment
- Photography lens
- Windows for optical systems and instruments
- Glass substrate
- Lead radiation glasses
- Precision lens
- Pressure sensor
- Laser system
- beam splitter
