Electron microscopy (EM) uses a beam of accelerated electrons as the source of illumination.
Since the wavelength of electrons is many times shorter than that of photons of visible light, electron microscopes have much higher resolution than conventional microscopes.
At the same time, due to the complexity and sensitivity of electron microscopy, the evaluation and selection of the site, room location, and environmental conditions must be carefully considered to achieve optimal performance of the electron microscope.
The two most common types of electron microscopes are the transmission electron microscope (TEM) and the scanning electron microscope (SEM). Transmission electron microscopy works with very thin samples under a vacuum.
For the laboratory where the electron microscope is placed, there are many factors that affect the environment of the laboratory, usually in the following aspects: vibration, magnetic field, and noise. These three aspects will interfere with the image of the electron microscope. Effects that affect the image.
Vibration:
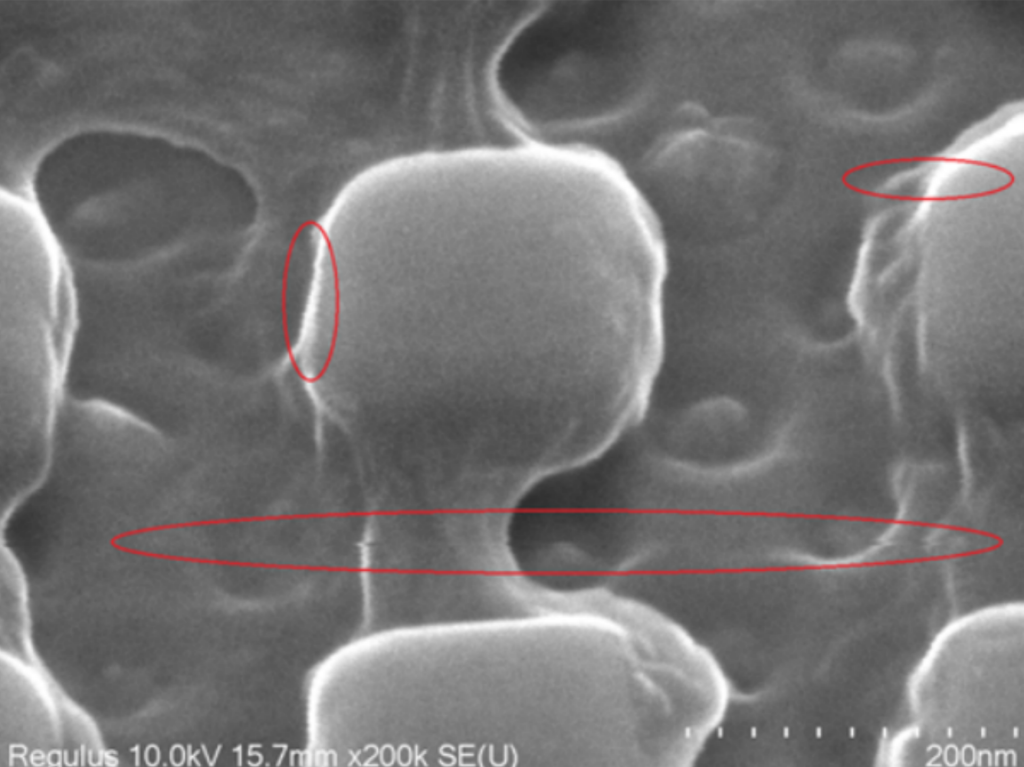
The micro-vibration is transmitted to the electron microscope, which causes the relative movement of the electron beam and the sample stage, thereby causing interference on the screen. The image feature of this interference is very similar to water waves, which are usually described as “sawtooth”.
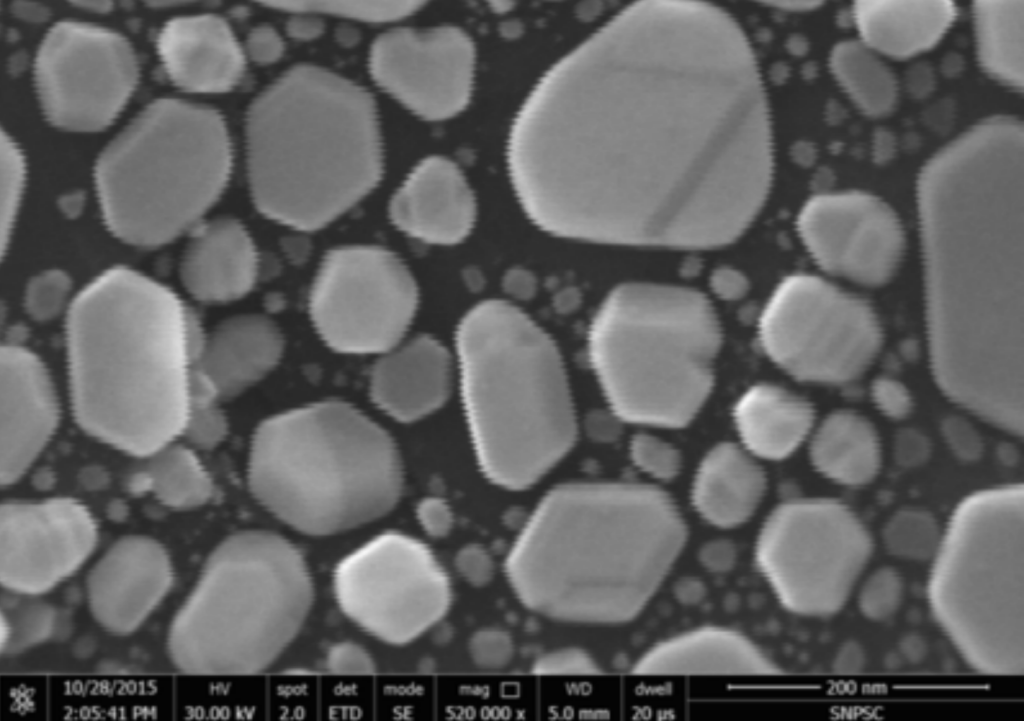
Magnetic field:
The magnetic field in the environment is divided into AC magnetic field and DC magnetic field, and their interference characteristics in the picture are different. The AC magnetic field usually forms a picture feature similar to vibration interference. The difference is that the ratio of the length to the height of the sawtooth is very large, usually reaching ten or twenty times. We call it a “glitch”.
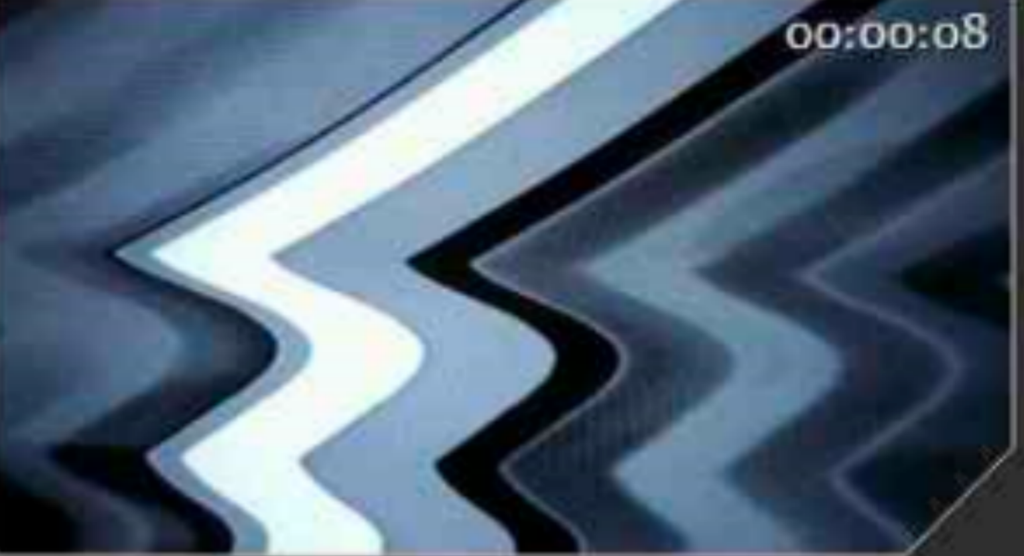
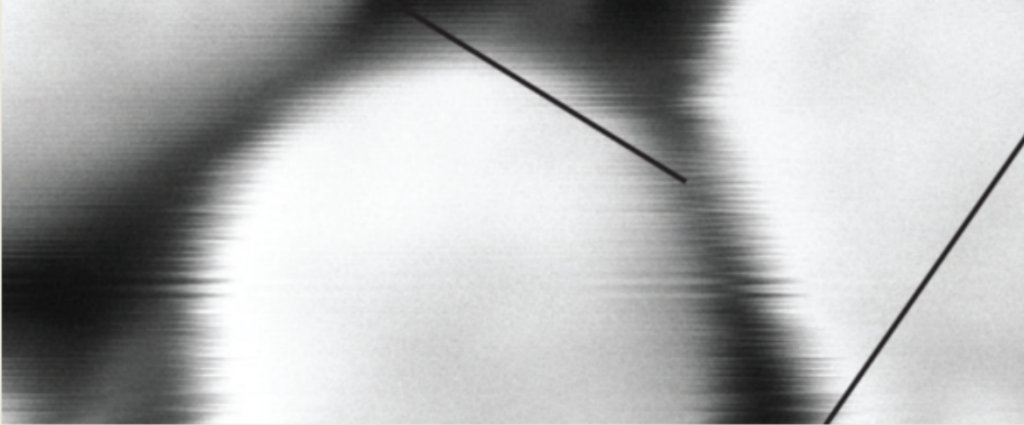

Noise:
The noise in the environment carries energy when it propagates in the air. When the noise hits the surface of the lens barrel of the electron microscope, if the frequency of the noise is close to the natural frequency of the lens barrel, it will cause the resonance of the lens barrel, thereby generating micro-vibration interference with the ground Very similar disturbances, ie like water waves.
Electron microscopes have strict requirements on the interference of vibration and external stray magnetic fields. The requirements of the installation environment are mainly considered from the aspects of laboratory space, power supply, temperature and humidity, noise, shockproof and antimagnetic, so the most important thing to pay attention to when choosing the installation location is These two aspects:
1. To reduce the interference of external vibration, the electron microscope laboratory should be as far away as possible from the elevator room and large equipment;
2. In order to reduce the interference of external magnetic fields, the electron microscopy laboratory should be as far away as possible from power stations and distribution rooms, as well as high-power electrical equipment.
Evaluation of Electron Microscope Design Parameters
Due to the complexity of the design and the high sensitivity of the electron microscope, a thorough assessment of the intended location of the facility is important. In order to determine whether the overall environment is suitable for equipment operation, several factors must be considered, such as vibration, noise, temperature control, differential pressure, electrical equipment magnetic field, and radio frequency noise.
• Vibration: Vertical vibration may cause image focus to spread and may limit achievable resolution. Horizontal vibrations directly distort the image. Vibrations can reach the electron microscope through floors (vehicle traffic, movement of heavy equipment, background vibrations from its own auxiliary equipment), HVAC systems (acoustic vibrations), footsteps, and other sources. Some vibrations may come from the building’s natural frequencies.
• Noise: The contribution of noise in electron microscopy can come from residual noise sources from AC fields or HVAC sources.
• Temperature control: Removal of heat from the microscope room requires air installations which may create noise and drafts which should be avoided.
• Pressure differential: Significant pressure differentials affecting the electromagnetic chamber may cause changes in the vacuum chamber and its controls.
• Magnetic Fields: Alternating Current Electromagnetic Interference (AC-EMI) is a common source of scanning noise. It needs to be determined whether the observed noise is from EMI or via vibration or acoustic coupling.
• Radio Frequency Noise: While electron microscopes are designed to block radio frequency noise, they may not be very effective at frequencies of 3000 Hz or lower.
Summarize
The influence of the above design parameters can negatively affect the performance of the electron microscope, resulting in suboptimal resolution. The following questions should be addressed early in the planning and design process:
Vibration and noise: Assess the building and the immediate area around the electron microscopy laboratory, paying special attention to mechanical and electrical equipment. Ensure that the building structure has adequate stability and vibration characteristics, and provide vibration damping and other remedial measures as required.
HVAC: Airflow in the tower should not exceed 20 ft/min, preferably less than 15 ft/min. Depending on the application, chilled beams, radiatively cooled panels or laminar diffusers should be considered.
Make sure the room is equipped with differential pressure control and that any door closing system does not produce hard closing impacts or extra loud closing sounds.