Features and Principles of Polarizing Microscopes
A polarizing microscope is used to study materials with both transparent and opaque anisotropic properties. Substances with birefringence can be clearly distinguished under a polarizing microscope. While staining methods can be used for observation, some materials require a polarizing microscope. Reflective polarizing microscopes are essential instruments for studying and identifying materials with birefringence, offering users the capability for simple polarization observation, orthogonal polarization observation, and conical light observation.
1. Key Characteristics of Polarizing Microscopes
Polarizing microscopes alter ordinary light into polarized light to identify whether a substance is uniaxial (isotropic) or biaxial (anisotropic). Birefringence is a fundamental characteristic of crystals. Therefore, polarizing microscopes find extensive applications in fields such as mineralogy, chemistry, biology, and botany. They are crucial for identifying fine structural optical properties of substances with birefringence.
2. Basic Principles of Polarizing Microscopes
● Uniaxial and Biaxial Nature
Materials are categorized as isotropic (uniaxial) or anisotropic (biaxial) based on whether light properties change with the illumination direction. Examples include gases, liquids, and non-crystalline solids for isotropic, and crystals, fibers, etc., for anisotropic.
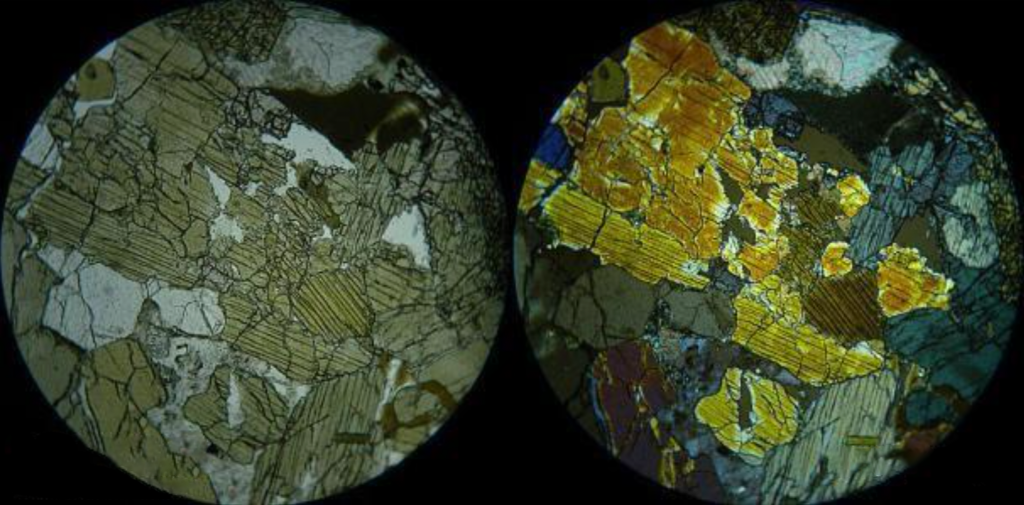
● Polarization of Light
Light waves can be categorized as natural light or polarized light based on their vibration characteristics. Polarized light refers to light waves vibrating in a single direction.
● Generation and Effects of Polarization
The polarizing device in a polarizing microscope, comprising a polarizer and analyzer, plays a crucial role. Synthetic polarizing mirrors, made of Herapathite crystals, have replaced natural Nicol prisms. The interaction between the polarizer and analyzer determines the brightness of the field of view.
● Biaxial Crystals in Orthogonal Position
In the orthogonal position, the field of view is dark for isotropic substances. However, biaxial substances exhibit bright areas due to the generation of two differently vibrating linearly polarized lights when the polarized light passes through them.

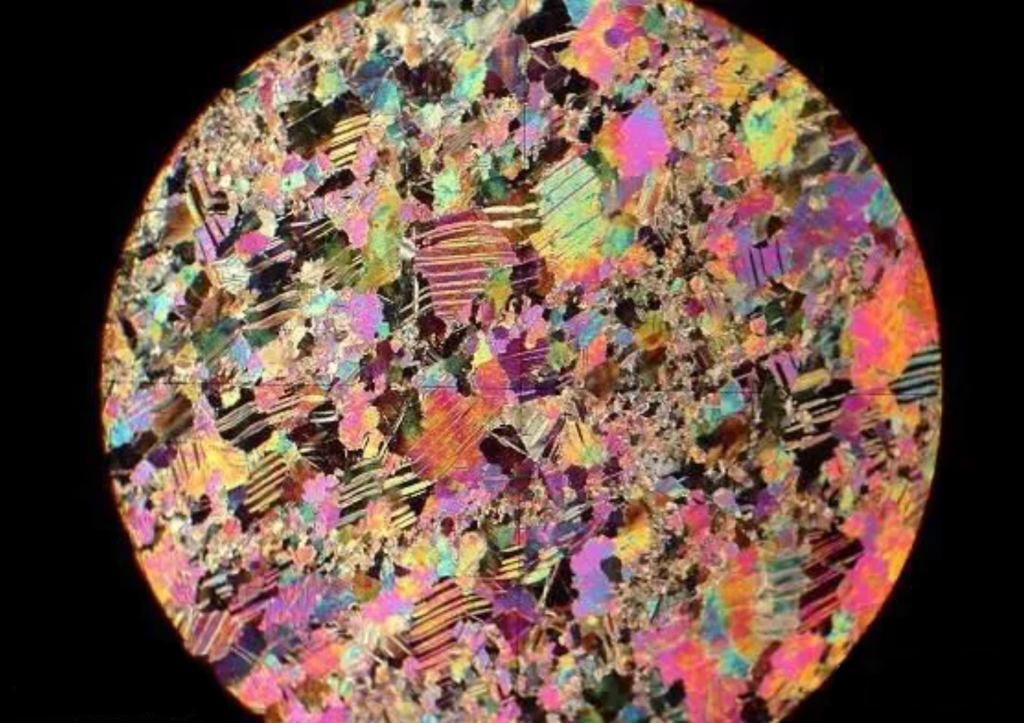
● Interference Colors
When observing biaxial substances in the orthogonal position with mixed light of different wavelengths, interference colors are visible due to interference effects. The distribution of interference colors depends on the type and thickness of the biaxial substance.
Performance of BM2100 POL Series Polarizing Microscope
- Capable of single polarization, orthogonal polarization, conical light, and digital photography observation, providing powerful functionality.
- It is equipped with gypsum, mica, quartz wedges, and other specimens for more accurate observation and research.
- Streamlined and highly stable design for smooth and convenient observations.
Technical Specifications of BM2100 POL Series Polarizing Microscope
| BM2100POL(T) | BM2100POL(T/R) | |||
| Observation System | Hinged binocular observation head, 30° inclination | ● | ● | |
| Hinged trinocular observation head, 30° inclination | ○ | ○ | ||
| Eyepiece | WF10X/20 | ● | ● | |
| WF10X/20 Crosshair Eyepiece | ● | ● | ||
| WF10X/20 Crosshair Graticule Eyepiece | ● | ● | ||
| Grid Plate | ● | ● | ||
| Infinity-Corrected Objective Lens Apochromatic Objective Lens | Transmitted/Reflected: 4X, 10X | ● | ● | |
| Transmitted: 20X, 40X, 60X | ● | ● | ||
| Transmitted: 100X | ○ | ○ | ||
| Reflected: 20X, 40X, 60X, 100X | ○ | |||
| Converter | Inward-type four-hole converter, center adjustable (one fixed hole, three adjustable holes) | ● | ● | |
| Vertical Illuminator | 12V/50W halogen lamp, adjustable brightness; variable aperture field diaphragm/field diaphragm | ● | ● | |
| Green, Gray Filters, Color Temperature Filters, and Frosted Glass | ● | ● | ||
| Polarizing Device | 0°-360° Rotatable Analyzer | ● | ● | |
| Bertrand Lens | Bertrand lens, adjustable center, adjustable focus, removable from optical path | ● | ● | |
| Optical Compensator | λ Plate (first-order red), 1/4λ Plate, Quartz Wedge Plate | ● | ● | |
| Circular Rotating Stage | Diameter Φ160mm, Graduation value 1°, Vernier value 6′ | ● | ● | |
| Condenser | NA0.9 Abbe condenser with variable aperture | ● | ● | |
| Focusing Adjustment | Coaxial coarse and fine focusing mechanism, focusing range 24mm, fine adjustment value 0.002mm | ● | ● | |
| Analyzer Rotation | 360° Rotatable with Filter | ● | ● | |
| Illumination System | 12V 50W halogen lamp or warm LED lamp, adjustable brightness | ● | ● | |
| Accessories | Photographic Attachment | 0.4X C Interface | ○ | ○ |
| 2X SLR Camera Interface | ○ | ○ | ||
| Mechanical Moving Scale, Moving Range: 30X40mm (including slice and specimen holder) | ○ | ○ | ||
| Flattening Machine | ○ | ○ | ||
| Micrometer | ● | ● | ||
| Color Temperature Filters | ● | ● | ||