Laser Confocal Microscopy Principle and Application
Introduction to Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy (LSCM):
LSCM is a high-tech microscope; it is equipped with a laser scanning device on the basis of fluorescence microscope imaging, and uses ultraviolet light or visible light to excite fluorescent probes to obtain fluorescent images of fine structures inside cells or tissues, which become morphological, A new generation of powerful research tools in the fields of molecular cell biology, neuroscience, pharmacology, genetics, etc.
Principle of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy (LSCM):
In ordinary wide-field optical microscopes, the entire specimen is illuminated by light from mercury arc lamps or xenon lamps, and images can be directly observed with the naked eye. At the same time, the fluorescence from other regions other than the focal point has a greater interference on the structure, especially when the thickness of the specimen is more than 2um, the influence is more obvious.
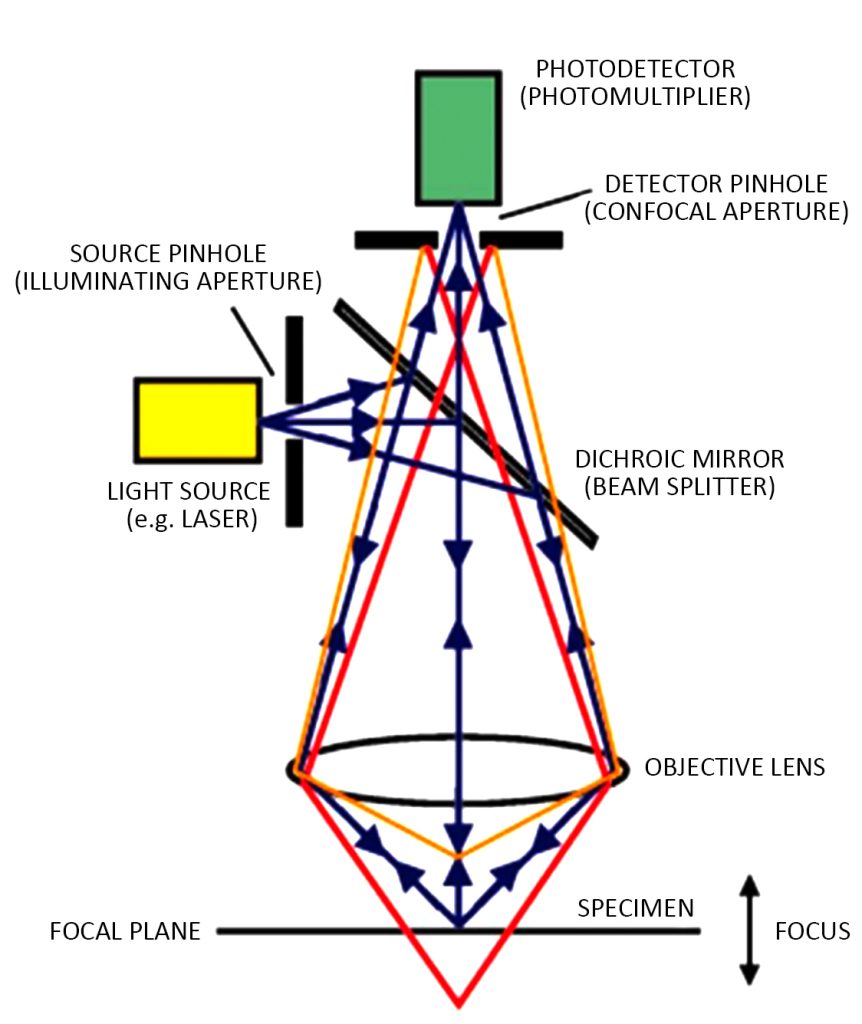
The laser confocal microscope breaks away from the field light source and local plane imaging mode of the traditional optical microscope and uses the laser beam as the light source. The laser beam passes through the illumination pinhole, reflects the objective lens through the beam splitter, and focuses on the sample. Scan at one point.
If there is a fluorescent substance that can be excited in the tissue sample, the fluorescence emitted after being excited will directly return to the beam splitter through the original incident light path, and focus first when passing through the detection pinhole, and the focused light is detected by the photomultiplier tube (PMT) Collect and send the signal to the computer, and display the image on the computer monitor after processing.
In this optical path, only the light at the focal plane can pass through the detection pinhole, and the light from the area outside the focal plane is defocused at the detection pinhole plane and cannot pass through the pinhole. Therefore, the background of the non-observation point is black, the contrast is increased, and the image is clear.
Since the illumination pinhole and the detection pinhole are conjugate with respect to the focal plane of the objective lens, the points on the focal plane focus on the illumination pinhole and the detection pinhole at the same time, and the points outside the focal plane will not be imaged at the detection pinhole, that is, the common focus.
The laser is used as the light source and the sample is scanned, and it is focused twice during the process, so it is called a laser scanning confocal microscope.
Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy (LSCM) Applications:
A confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) is one of the most advanced cell biomedical analysis instruments in modern times.
It installs a laser scanning device on the basis of fluorescence microscope imaging, uses ultraviolet light or visible light laser fluorescent probes, and uses a computer for image processing. It can not only observe fixed cells and tissue slices but also analyze the structure and molecules of living cells. , ions for real-time dynamic observation and detection.
Laser scanning confocal microscopy technology has been used in the study of cell morphology localization, three-dimensional structure reorganization, dynamic change process, etc., and provides practical research methods such as quantitative fluorescence measurement, quantitative image analysis, etc., combined with other related biological technologies, in morphology, physiology, Immunology, genetics and other fields of molecular cell biology have been widely used.
