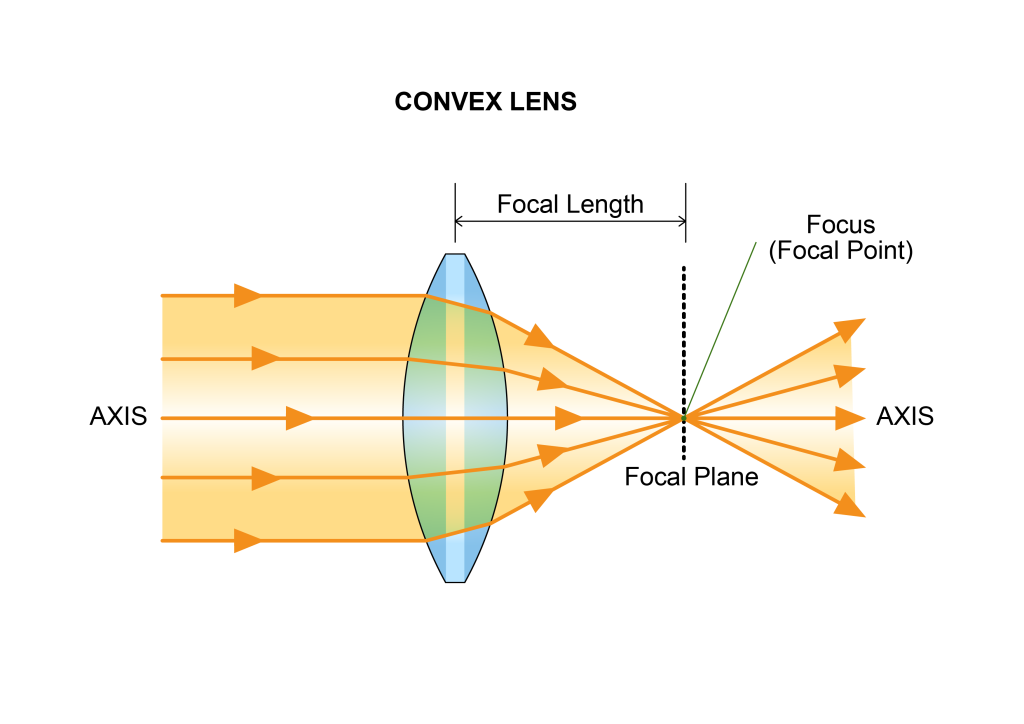
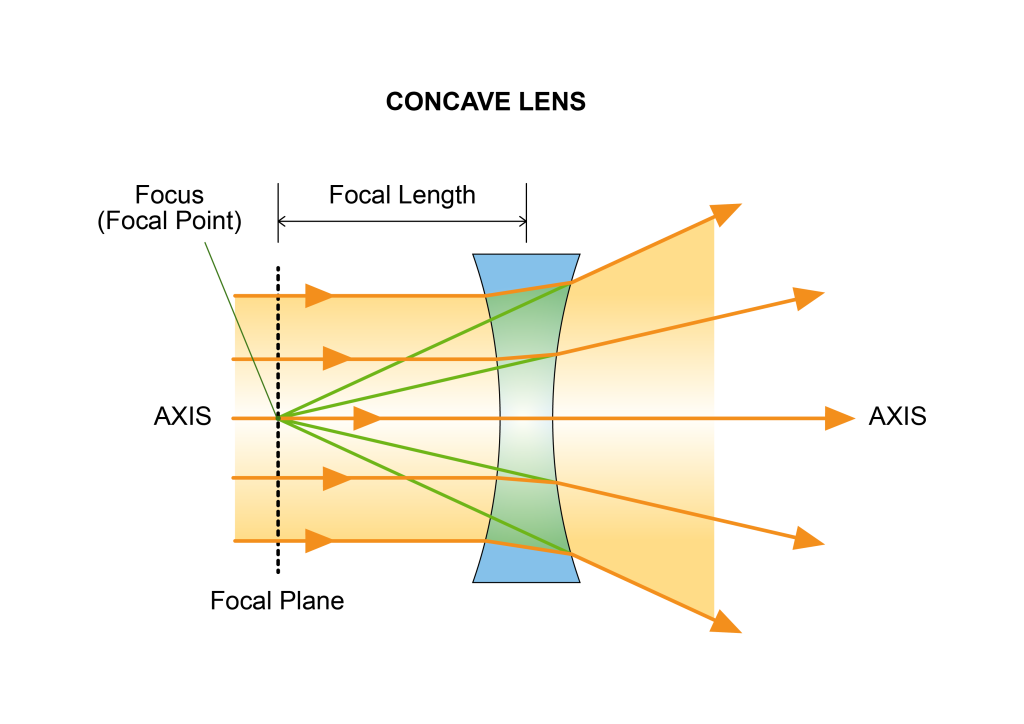
All optical lenses have a focal length, which is the distance from the lens to the focal point along the optical axis of the lens.
Three factors determine the focal length of a lens; the radius of curvature of the lens, the refractive index of the substrate from which the lens is made, and the medium in which the lens is placed.
A highly curved lens made of a high-index material, placed in a medium with a large difference in index of refraction, has a shorter focal length and is therefore more powerful.
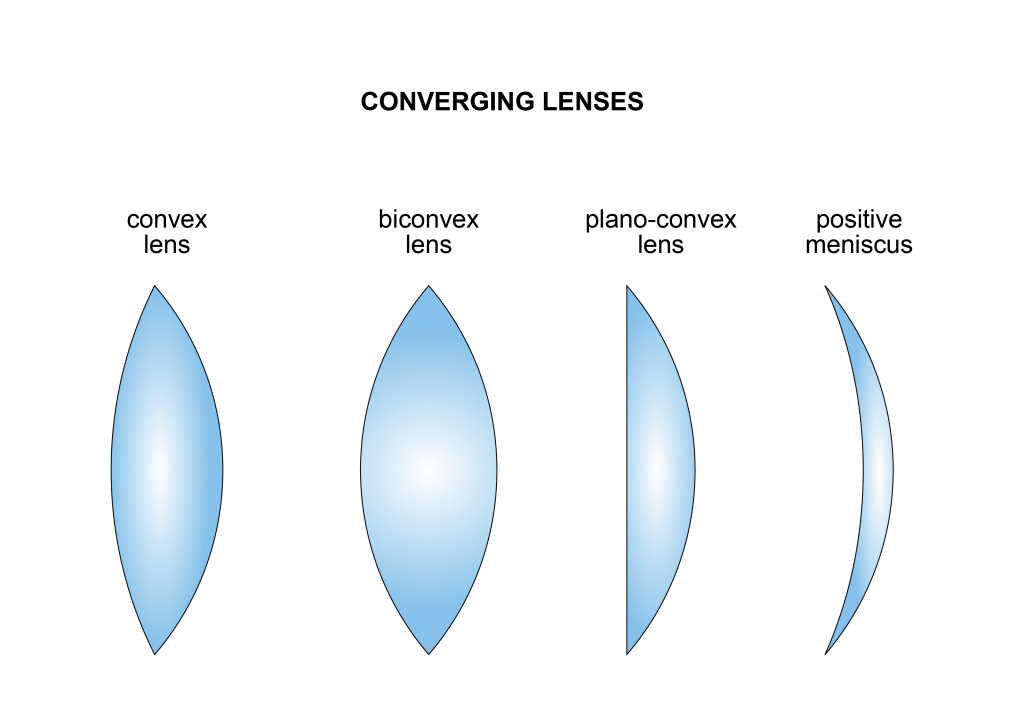
convex lens
Convex lenses bulge outward from the center, are thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges, and converge light rays parallel to the optical axis to a focal point outside the lens. Therefore, they can also be called positive lenses or converging lenses. The focal point is the point where collimated light rays converge and focus.
Generally, thicker convex lenses have the effect of far-sightedness and convergence, and the more common hyperopia glasses are made of convex lenses.
Convex lenses can be fabricated in different configurations such as biconvex, plano-convex, or positive meniscus.
concave lens
Concave lenses curve inward from the center, are thinner in the center and thicker at the edges, and diverge light rays parallel to the optical axis from a focal point behind the lens. Therefore, they can also be called negative spherical lenses or diverging lenses. The focal point is the point at which collimated light rays diverge after passing through the lens.
The images formed by the concave lens are all upright and reduced virtual images. Its most common use in life is to correct myopia.
Concave lenses can be fabricated in different configurations such as biconcave, plano concave, or negative meniscus.
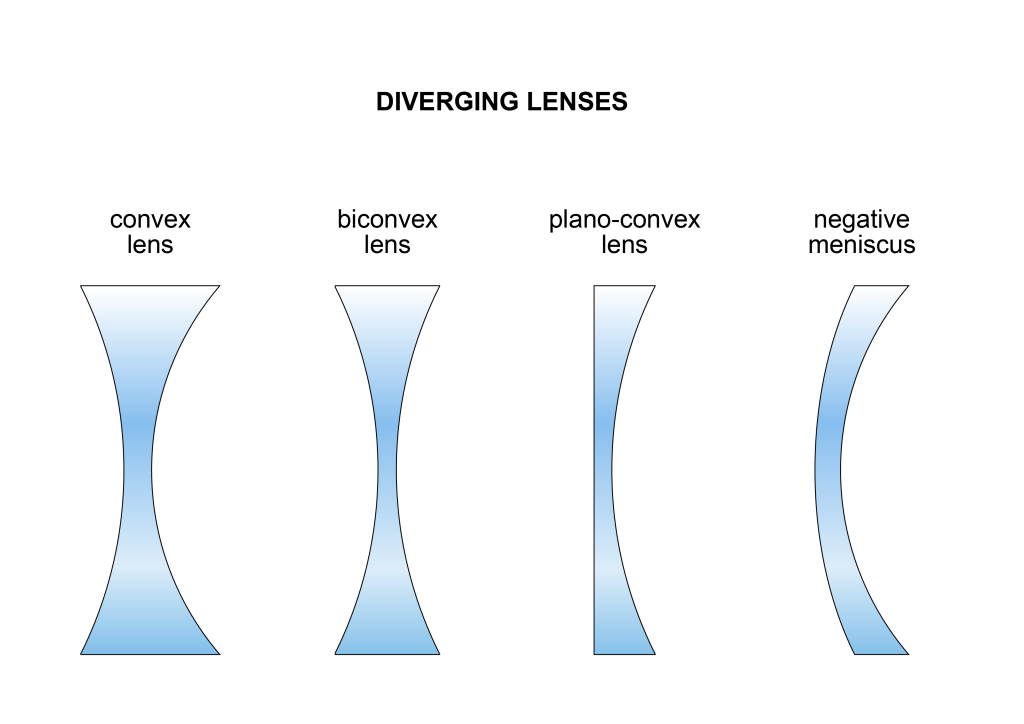
convex/concave mirror
Optical lenses can be made into convex and concave mirrors by adding reflective coatings. However, since the mirror reflects light instead of transmitting it, the focal point is reversed. As with lenses, the more curved a mirror is, the shorter its focal length, and therefore the more powerful the mirror will be.
convex mirror
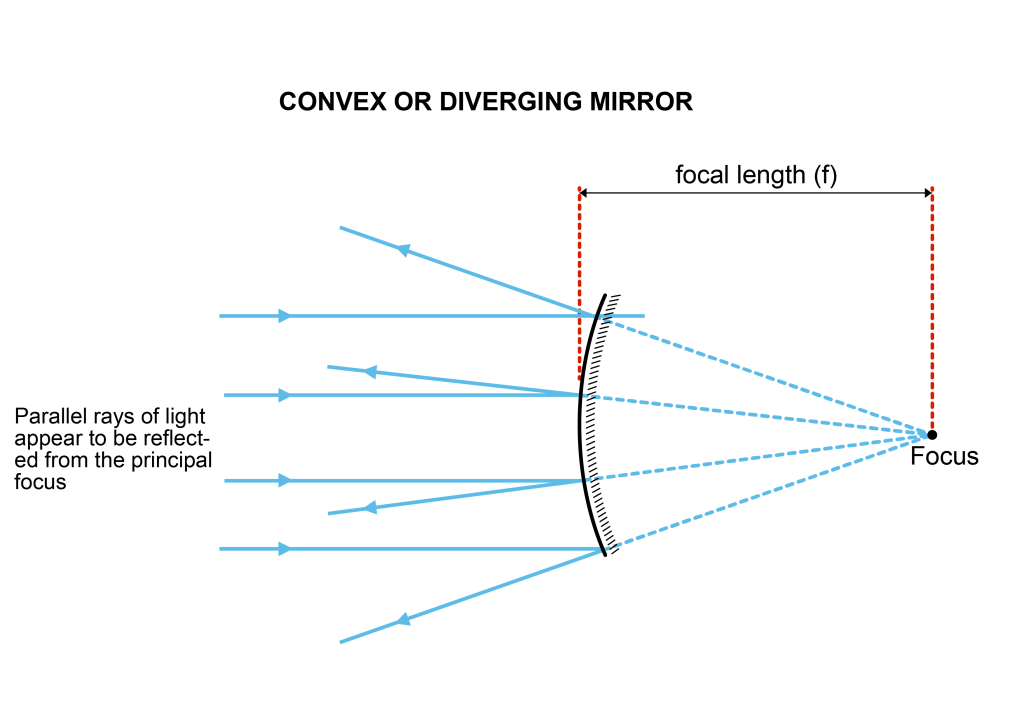
Convex mirrors (diverging mirrors) have surfaces that curve outward so that collimated light diverges from the reflective surface. The focal point is behind the mirror and is called the negative focal point. The light appears to be bouncing off the mirror.
concave mirror
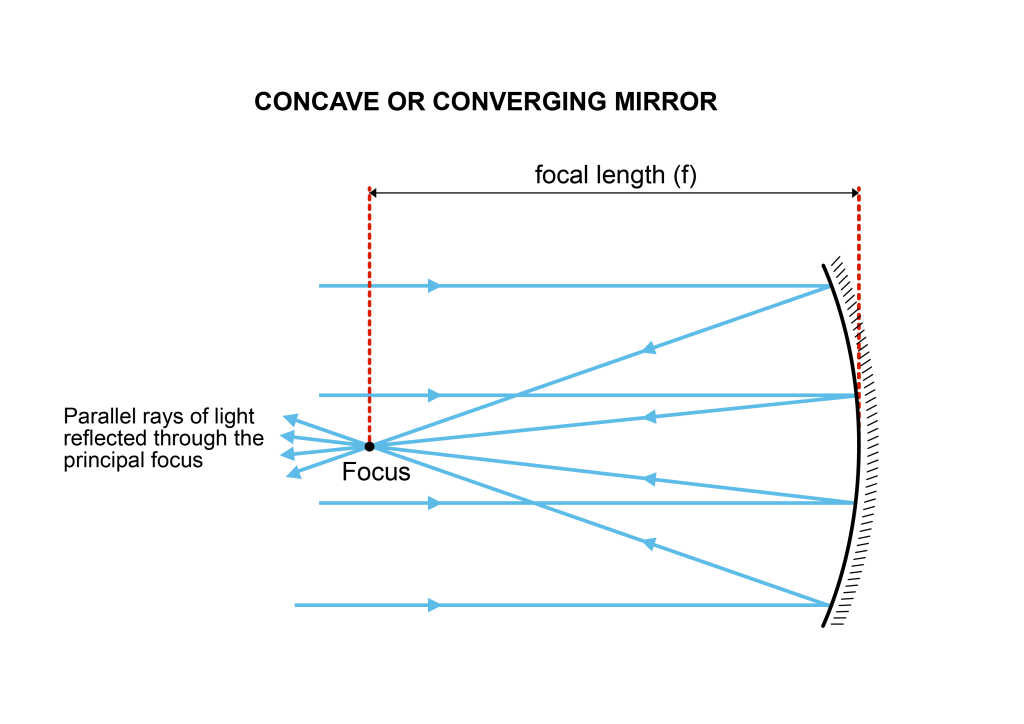
Concave mirrors (focusing mirrors) have surfaces that are curved inwards and thus collect collimated light. The focal point is in front of the mirror and is called the positive focus. It is the point where parallel beams of light are focused after being reflected by a mirror.
The Difference Between Convex/Concave Mirrors
- The structure is different. A convex mirror is composed of a transparent mirror body ground into a spherical surface on both sides. A concave mirror is composed of a mirror body that is concave on one side and opaque on the other.
- Different effects on light. Convex mirrors mainly refract light. Concave mirrors mainly reflect light.
- Imaging properties are different. Convex mirrors can form upright magnified virtual images, inverted magnified real images, inverted and other large real images, and inverted reduced real images. Concave mirrors can only form upright and reduced virtual images.
- The focus is different. A convex mirror has a real focal point and has 2 focal points. Concave mirrors have virtual focal points.
- Different uses. Convex mirrors are used for distance vision glasses. Concave mirrors are used for myopia glasses.
