ED glass stands for Extra Low Dispersion.
Dispersion occurs when colors are spread out by wavelength, like a rainbow effect. Since this also occurs in lens systems, some lens elements can be made from ED glass to minimize dispersion and resulting chromatic aberration.
1. What is optical dispersion?
First, before we discuss how one glass is better than another, let’s first clarify what dispersion is and what it means in the world of optics:
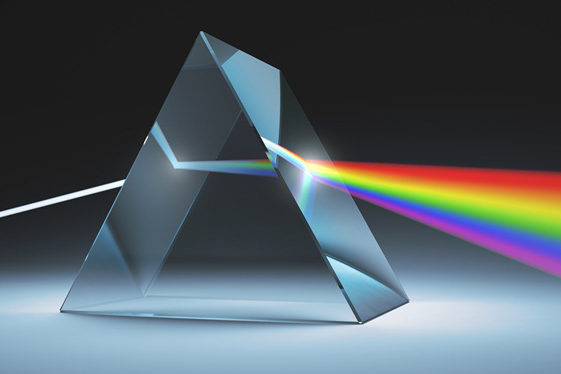
We all know that if you pass light through a prism, it breaks up white light into its component colors. The blue end of the spectrum is the most curved and the red end is the least curved.
So a prism spreads or disperses, the colors that make up white light, and dispersion is simply a measure of how much the colors are spread.
2. How to reduce glass dispersion
A. Achromatic principle of low dispersion glass
Low-dispersion glass is a kind of glass manufactured according to a reasonable design of optical constants. Through precise control of optical constants such as the refractive index and dispersion rate of light, it can be formulated as a material with a small dispersion rate.
Achromatism refers to the chromatic aberration phenomenon caused by the different dispersion of light when light passes through optical components such as lenses and prisms.
Low-dispersion glass achromatic technology uses different methods to eliminate chromatic aberration in optical components.

B. The method and technology of low dispersion glass achromatic
- Dispersion ratio matching: By pairing two materials with opposite dispersion characteristics, the effect of eliminating chromatic aberration can be achieved.
- Composite glass structure design: By designing the composite glass structure, different parts can produce opposite dispersion effects, so as to eliminate or weaken the effect of chromatic aberration.
- Anti-dispersion coating: Coating is a technology that achieves optical effects through a thin film attached to the glass surface. Anti-dispersion coating is to coat a layer of film with opposite reflectivity on the glass surface to eliminate or weaken the effect of chromatic aberration.
3. Other characteristics of low dispersion glass:
1. The temperature stability of low-dispersion glass is not as good as that of traditional glass, so the focal length of these lenses changes slightly with temperature;
2. Low-dispersion glass also has a lower index of refraction, so a deeper curved element is required at the same focal length.
4. Application of low-dispersion glass
Extra-low dispersion glass prevents or reduces chromatic aberrations because it gives designers of multi-element objectives more options for concentrating and directing wavelengths of light more efficiently so that aberrations, especially chromatic aberrations, can be controlled and minimized.
In general, the better the aberrations are controlled, the cleaner and brighter the image will appear.
Low-dispersion glass is widely used in high-definition projectors, optical lenses, spectacle lenses, telescopes, and other fields.
5. Summary
With the continuous development of science and technology, low-dispersion glass achromatic technology continues to break through and innovate. Most high-end optical devices are now equipped with ultra-low dispersion glass lenses, which provide strong support for the development of various high-precision optical equipment.
As a high-performance optical material, low-dispersion glass has broad application prospects and will play an increasingly important role in various optical fields in the future.
