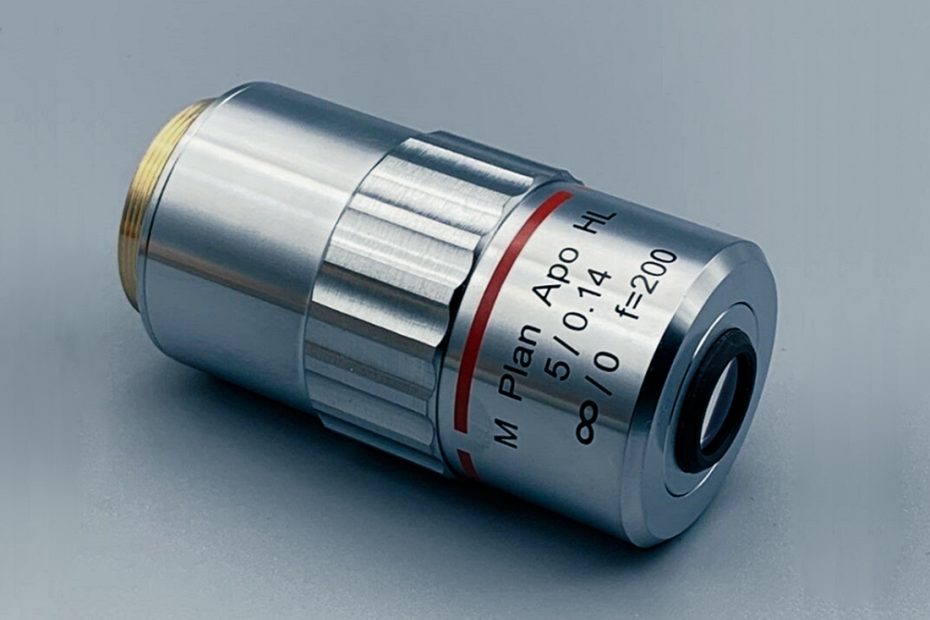
Microscope objective lens parameters

Figure 1
1. Magnification
“10” and “4” in the first row of numbers on the objective lens indicate that the objective lens has a magnification of 10 times or 4 times. The magnification here is not the magnification of the area, but the length or width of the image. Magnification and the total magnification of a microscope is equal to the product of the magnification of the objective and eyepieces.
2. Resolution
Resolution refers to the minimum distance between two object points that can be distinguished. The smaller the resolution distance of a microscope, the higher its resolution, which means the better its performance. The resolution of a microscope is determined by the resolution of the objective lens, which is determined by its numerical aperture (lens ratio) and the wavelength of the illuminating light. When light passes through the specimen uniformly, the resolution distance of the microscope can be expressed by the formula: D=0.61λ/NA (D represents the resolution distance of the objective lens, in nm; λ represents the wavelength of the illumination light, in nm; NA represents the numerical aperture of the objective lens) , so the resolution of the microscope is proportional to the numerical aperture. (The smaller the D value, the higher the resolution)
3. Numerical aperture (lens ratio)
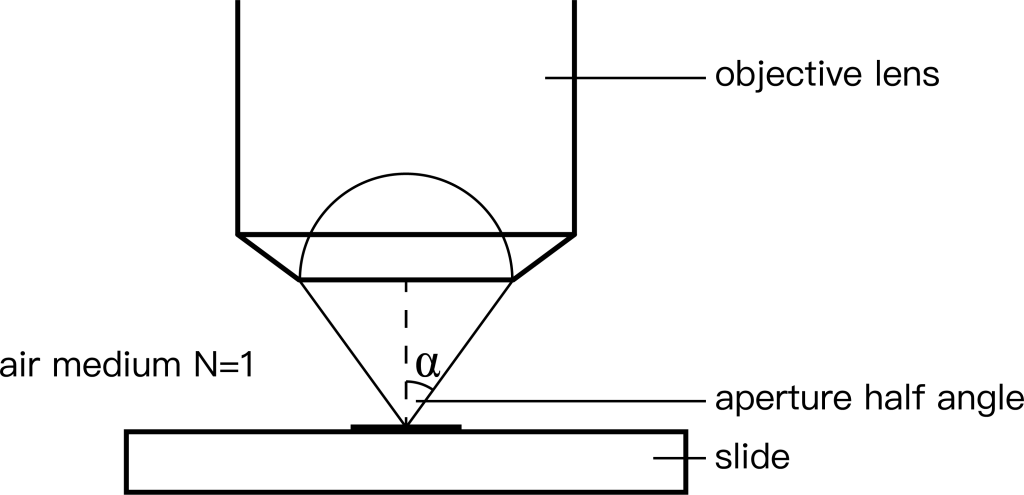
“0.25” and “0.10” in the objective lens are the numerical apertures of the two objective lenses respectively. They represent the ability of the front lens of the objective lens to collect light from the sample. The size of the numerical aperture can be determined by the formula NA=Nsinα, where N represents the refractive index of the medium, N=1 in air, and under an oil lens, N can be increased to 1.5; α represents the objective lens aperture half angle (Figure 2). The larger the objective lens aperture half-angle, the more light enters the objective lens. .
4. Mechanical tube length:
The “160” on the objective lens in Figure 1 means that the objective lens must be used on a microscope with a mechanical tube length of 160mm. The distance from the objective lens positioning surface to the eyepiece positioning surface is 160mm. This distance is called the mechanical tube length, which is the length of the remaining lens tube after the objective lens and eyepiece are removed. Countries have different regulations on mechanical barrel length, mainly including 160mm, 170mm, and 190mm.
5. Cover glass thickness

According to international regulations, the standard thickness of the cover glass is 0.17±0.01mm. The number “0.17” marked on the objective lens in Figure 1 indicates that the objective lens requires the thickness of the cover glass to be 0.17mm. If the thickness of the cover glass is greater than 0.18mm, stray light (not light reflected by the mirror) will enter the objective lens, thus producing a phase difference. When the thickness of the cover glass is less than 0.16mm, the light that should enter the objective lens cannot enter the objective lens, which in turn produces phase difference and affects the observation effect. In addition, since the refractive index of cedar oil and glass are similar, the oil lens objective lens does not have the phase difference problem caused by the irregular thickness of the cover glass. In other words, the thickness of the cover glass has almost negligible influence on the observation effect of the oil lens objective lens. It can be used with or without a coverslip (such as a blood smear). Therefore, some oil lenses are not marked with “0.17” but replaced with a horizontal line “-“.
6. Working distance
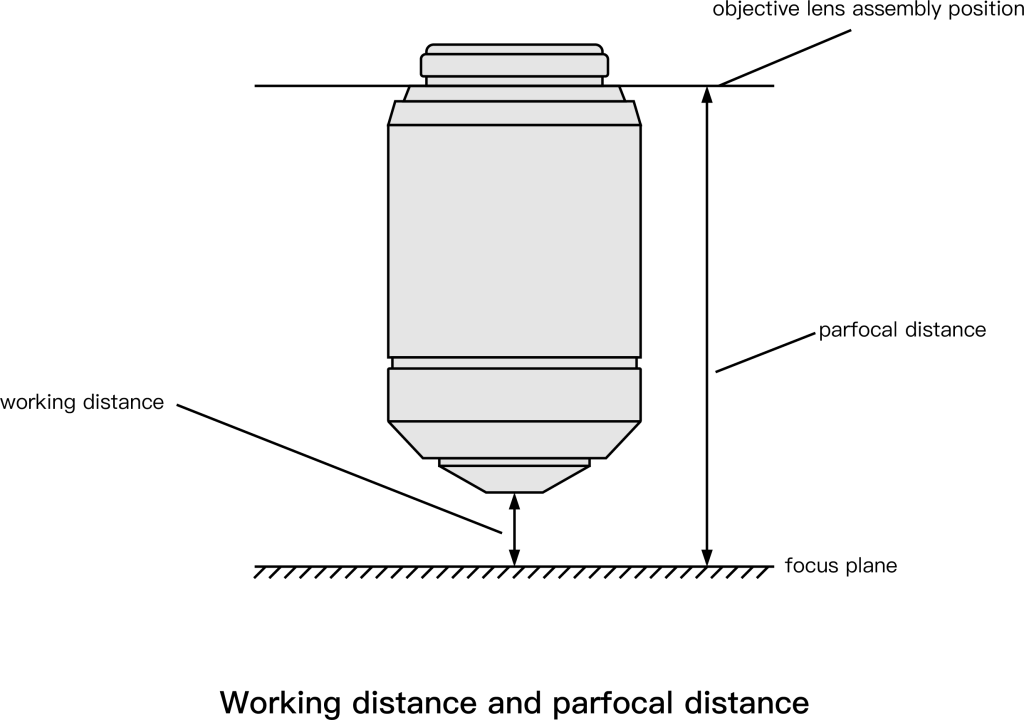
The working distance is also called the object distance, which refers to the distance between the surface of the front lens of the objective lens and the object being inspected.
Summarize
As shown in the figure, the meanings of the four data in the figure are:
- ①The “10” and “4” in the first row of numbers on the objective lens indicate the magnification of the objective lens.
- ② “0.25” and “0.10” in the objective lens are the numerical apertures of the two objective lenses, that is, the lens opening ratio, which is related to the resolution of the microscope. The larger the number, the higher the resolution, which means the better its performance.
- ③The “160” on the objective lens is called the mechanical tube length, which means that the distance from the objective lens positioning surface to the eyepiece positioning surface is 160mm. That is, the length of the remaining lens tube after removing the objective lens and eyepiece means that the objective lens must be in the mechanical lens tube. Can only be used on microscopes with a length of 160mm.
- ④The number “0.17” marked on the objective lens indicates that the objective lens requires a cover glass thickness of 0.17mm.
