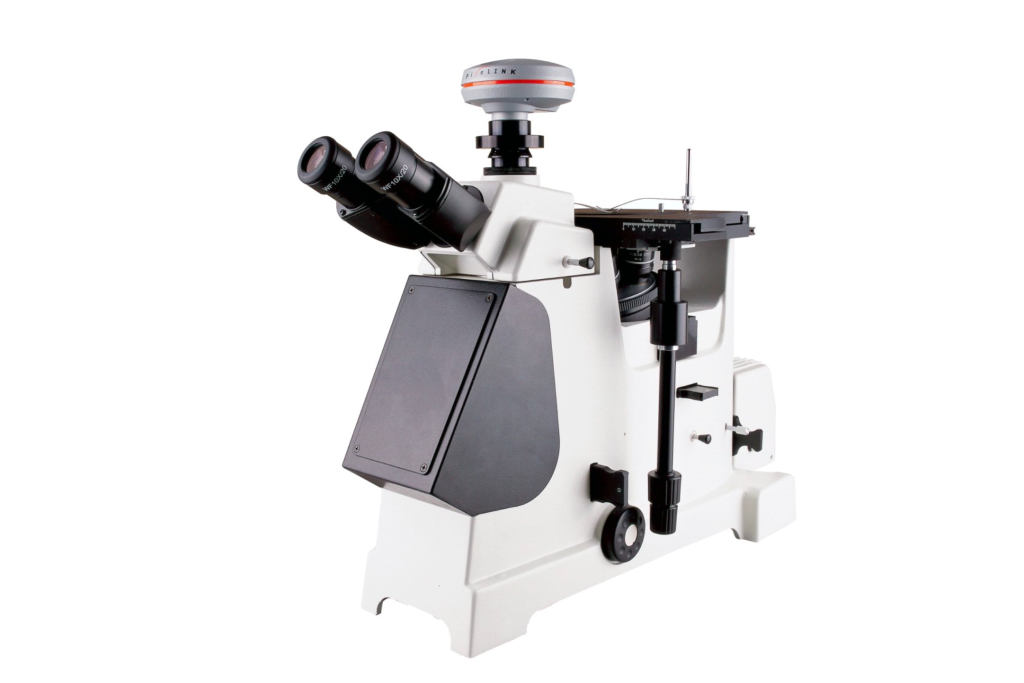

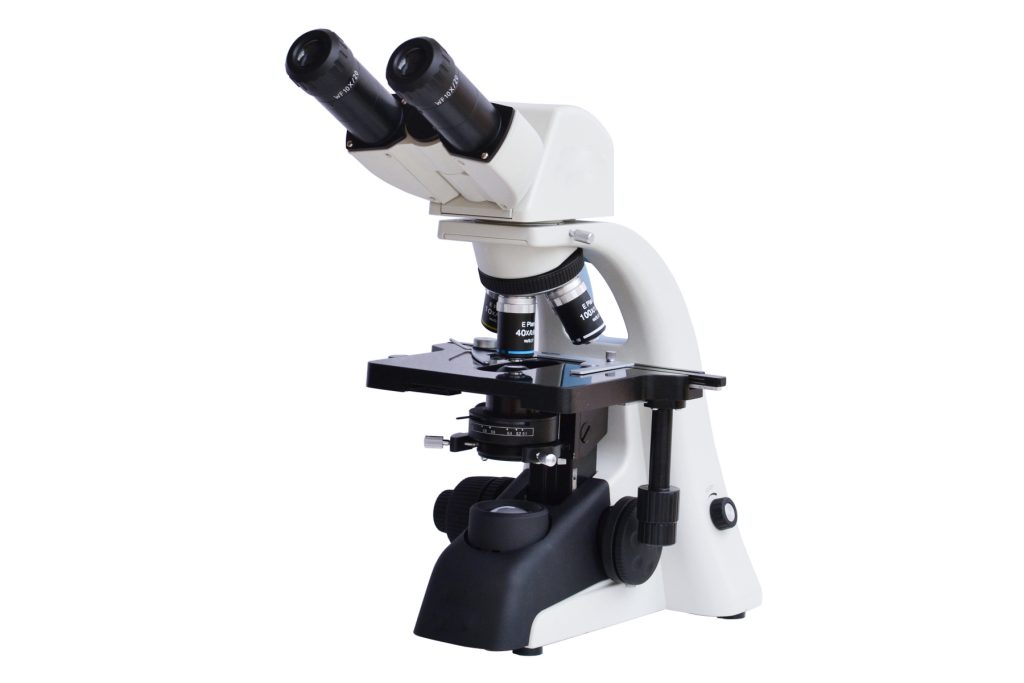
1. What is a metallographic microscope and its application fields?
Metallographic microscopy: Metallography mainly refers to the branch of materials science that analyzes, studies, and characterizes the microstructure, low-magnification structure, and fracture structure of materials with the help of optical metallographic microscopes and stereo microscopes. It includes both the imaging of material microstructure and its Qualitative and quantitative characterization, including necessary sample preparation, preparation, and sampling methods.
The metallographic microscope mainly reflects and characterizes the phase and structural composition of the material, the number, morphology, size, grains (including possible sub-grains), non-metallic inclusions, and even some crystal defects (such as dislocations). Distribution, orientation, spatial arrangement, etc.
Used for structural analysis of PCB circuit board sampling cross-section circuits and image analysis of LCD circuits and liquid crystal balls.
It has: high-definition image observation and data measurement of copper thickness on the end face and hole of circuit board sampling parts, observation and data measurement of green oil and white oil. At the same time, the software has the functions of image freezing, data measurement, and report output.
The LCD monitor can observe: images of OLB, liquid crystal ball and gold finger pressing form in DIC and offset.
2. Four major advantages of metallographic microscopes
- A collection of multiple technologies
The four major advantages of a metallographic microscope? A metallographic microscope itself is a metal observation microscope. It mainly uses incident illumination to observe the metallographic structure of the surface of metal samples. People usually use it to study the metallographic structure of heat-treated materials. in the work of the organization. It is an optical instrument that integrates optical microscope technology, photoelectric conversion technology, and computer image processing technology.
- Excellent functions
It has a compact structural layout, and its appearance is also very beautiful and elegant, making it more convenient to use. Based on its collection of corresponding technologies, the imaging is clearer and the field of view is wider. The overall design is more in line with human-machine functions and can Withstand this long operation.
- Well designed
The base area of the metallographic microscope is very large, so the area it can support is also very wide. The strong bending arm strength makes the center of gravity of the instrument lower, and people can achieve stable and reliable placement during use. Effect.
- Great effect
Metallographic microscopes are used to identify and study the organizational structures of various metals, alloy materials, and non-metallic substances, which also involve observing the surface conditions of integrated circuits, microparticles, etc.
Generally, metallographic microscopes will appear in metallurgy, shipbuilding, quality inspection, and industrial and mining enterprise laboratories. At the same time, reflected light imaging is used when illuminating, so it must have a special vertical lighting device to improve certain tissues. contrast.
1. What is a biological microscope and its application fields?
Biological microscope: used by medical and health units, colleges and universities, and research institutes to observe microorganisms, cells, bacteria, tissue culture, suspensions, sediments, etc., and can continuously observe the process of reproduction and division of cells, bacteria, etc. in the culture medium. It is widely used in the fields of cytology, parasitology, oncology, immunology, genetic engineering, industrial microbiology, botany and other fields.
Important Optical Technical Parameters of Microscopes During microscopic examination, people always hope to have a clear and bright ideal image, which requires the various optical technical parameters of the microscope to reach certain standards, and it is required that when used, it must be based on the requirements of microscopic examination. To coordinate the relationship between each parameter according to the purpose and actual situation. Only in this way can we give full play to the performance of the microscope and obtain satisfactory microscopic examination results.
The optical technical parameters of the microscope include numerical aperture, resolution, magnification, focal depth, field of view width, coverage difference, working distance, etc. These parameters are not always higher, the better. They are interconnected and restrictive. When used, the relationship between parameters should be coordinated according to the purpose of microscopy and the actual situation, but the resolution should be guaranteed.
2. Four major advantages of biological microscopes
- High resolution and high magnification
Biological microscopes use advanced optical technology, have high resolution and high magnification, and can observe cells and fine internal structures of cells, such as organelles, DNA, RNA, etc. High resolution and high magnification make the observed samples clearer and more accurate, providing a strong experimental basis for biological research.
- A wide range of observed samples
Biological microscopes can be used to observe various biological samples, including cells, tissues, bacteria, viruses, etc. Its wide observable range provides convenience for biological research in different fields.
- Ability to perform multiple staining of samples
Biological microscopes enable multiple staining of samples to better visualize and distinguish different cellular structures and substances. Multiple staining technology can increase the reliability and accuracy of experimental results.
- With the image processing function
Modern biological microscopes are usually equipped with image-processing functions that can digitally process and analyze the observed cell images. These capabilities facilitate more accurate quantitative analysis of cellular structures and material characteristics.
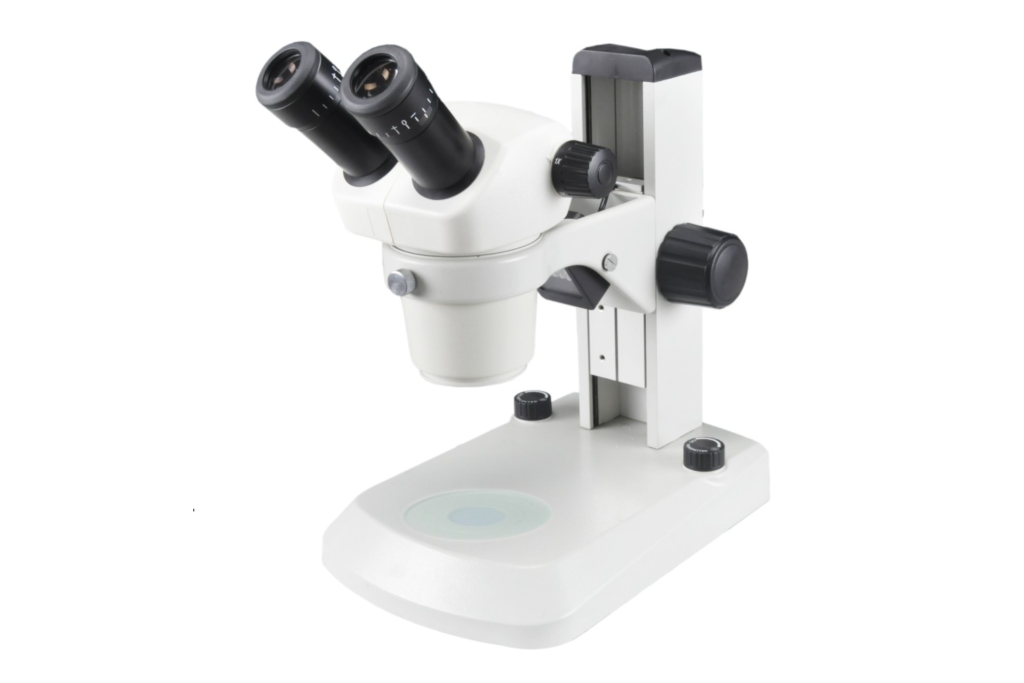
1. What is a stereo microscope and its application fields?
Stereo microscope: also known as “solid microscope”, “stereo microscope” or “operating and dissecting microscope”, it is a microscope with an upright three-dimensional sense and is widely used in material macro surface observation, failure analysis, and fracture analysis. and other industrial fields. It is a visual instrument with an upright three-dimensional sense and is widely used in various departments of biology, medicine, agriculture, forestry, industry, and marine biology.
2. Five major advantages of stereo microscopes
- The left and right light beams in the binoculars are not parallel but have a certain angle of view (usually 12 degrees to 15 degrees), so the image has a three-dimensional sense;
- The image is upright and easy to operate and dissect. This is because the prism under the eyepiece inverts the image;
- Although the magnification is not as good as that of a conventional microscope, its working distance is very long
- The depth of focus is large, making it easy to observe the entire layer of the object being inspected.
- Large field of view diameter.