The principle, structure, application, and advantages and disadvantages of dissecting a microscope
A dissecting microscope (also known as a stereo microscope), is so called because it helps you better visualize a specimen or sample while performing a dissection. Dissecting microscopes are digital light microscopes designed for low magnification (5x-250x), utilizing light reflected from the surface of the specimen, rather than light reflecting off the specimen.
Its main role is to dissect specimens, and observe and qualitatively analyze dissected samples.
Dissecting microscope (stereo microscope) principle
The operating principle of a dissecting microscope is based on two light paths used by the microscope objective and eyepiece. Each light path offers a unique perspective. Dissecting microscopes have an overhead light for dissection and a bottom light for viewing photographs.
This illumination is allowed by the design of two eyepieces (binocular stereoscopes), each presenting a different type of light path and providing a viewing comfort zone.
The photos are displayed in real-time on a computer monitor in 3D visuals because it is a digital microscope.
Dissecting microscopes also allow very close observation of tiny specimens, such as insects, with images often larger than the sample size, a phenomenon known as macro photography. Record images and examine the topography (surface) of complex samples in 3D.
Dissecting microscopes have two magnification systems: fixed (primary) magnification, which uses two objectives to provide a certain degree of magnification, and zoom (pancratic) magnification, which uses auxiliary objectives to provide continuous magnification over various ranges, based on a number of factors. Eyepieces can be interchanged to achieve magnification differences between zoom and fixed magnification.
Between the fixed magnification and the zoom magnification is the Galilean optical system, which is characterized by a fixed focus lens that provides a fixed magnification for various magnifications, such as two sets of magnifications providing four times magnification and three sets of magnifications providing six times magnification rate, and so on.
Parts of a Dissecting Microscope
Dissecting microscope components include an objective lens and two eyepieces. There are two independent light paths that transmit the image of the specimen to each eyepiece. The beam of light comes from above the specimen. Since we have binocular vision, our eyes see images with overlapping fields of view, allowing for the perception of depth. The result is an outstanding three-dimensional image of the specimen under study.
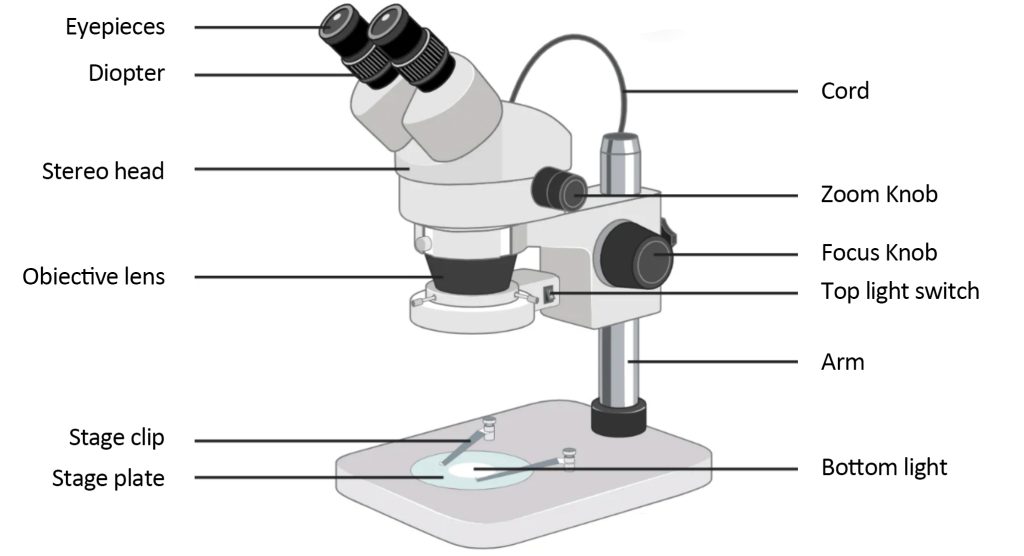
A typical dissecting microscope has 6 main parts:
LED Illuminator: Typically, dissecting microscopes have an LED light that illuminates the exhibit to be viewed.
Eyepieces: Every dissecting microscope has two eyepieces for focusing light with diverging paths. One path enters the sample and the other exits the sample. Both eyepieces have different magnifications. To increase magnification, the microscope employs auxiliary eyepieces.
Objectives: Objectives are similar to eyepieces and have different magnifications that can be used to focus on a specimen. This lens can be used to focus the image on a digital camera, with auxiliary objectives used to increase magnification.
Stage: As the name suggests, the stage is where the specimen is placed for viewing through the microscope, in some types of dissecting microscopes the stage is large to allow viewing of larger specimens
Optical system: The optical system is installed between the fixed magnification and the zoom magnification to provide a fixed focal length lens
Digital Camera: A digital camera is not technically part of a dissecting microscope, but it is often used to capture magnified images and also to capture video that can be used for further analysis.
Dissecting Microscope Applications
Dissecting microscopes use low magnification and offer a wide range of uses. It is used in applications in the following areas:
1. Study the morphology of solid samples
2. For dissection
3. Used in microsurgery
4. Used in the manufacture and inspection of watches and circuit boards
5. Used to check fractures (fractures)
6. For forensic engineering
The dissecting microscope, like most microscopes, is used in a wide variety of applications in manufacturing, medical, quality control, inspection, and biomedical research.
Advantages of Dissecting Microscopes (Stereo Microscopes)
It can be used in a wide range of fields, making it one of the most important microscopy techniques.
The use of two light paths provides a large magnification difference for visualizing images.
Accessories for digital cameras allow recording and imaging of the resulting images.
It is portable and easy to use.
They are used to view whole specimens rather than fragments.
