1. What is a stereo microscope

A stereo microscope, also known as a “solid microscope”, “stereo microscope” or “dissecting microscope“, is a microscope with a three-dimensional sense of positive image, which is used in the macroscopic surface observation of materials, failure analysis, fracture analysis, biology, medicine, Agriculture, forestry, industry and various application scenarios.
Stereo microscopes use two independent optical paths, and the two light beams after imaging the object are separated by two sets of intermediate objective lenses — zoom lens groups, and form a certain angle called the stereoscopic viewing angle, generally 12 degrees – 15 degrees, and then through the respective eyepieces, the images enter the two eyes of the person respectively, and the images of the specimens seen by each eye are different. This extra information allows the brain to reconstruct a three-dimensional image of the object by fusing the left and right images. Therefore, the imaging of a stereo microscope has a three-dimensional effect that a conventional upright microscope or an inverted microscope does not have. Stereo microscopes are the tool of choice when one needs to interact with specimens (such as dissection, screening, micro-engraving, micromanipulation, etc.).
2 The principle of stereo microscope and common stereo microscope
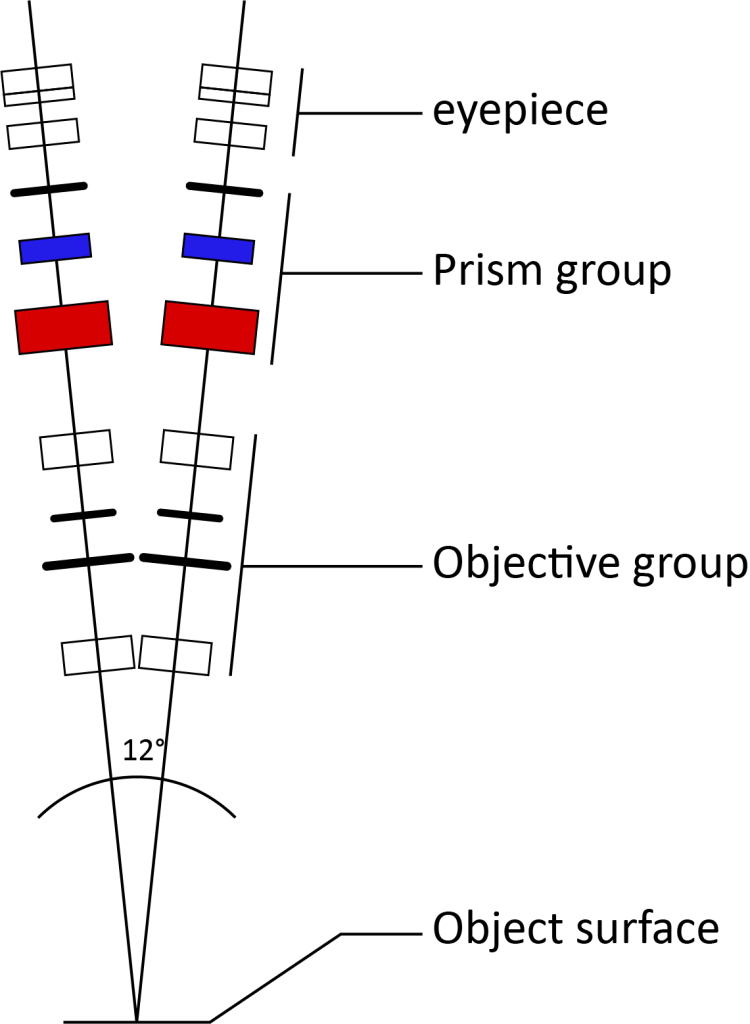
There are two main types of light path designs for stereo microscopes: Greenough Design and CMO Design. The schematic diagram of the Greenough light path is as follows:
Greenough’s principle: Two identical independent optical systems are attached to the same support at an angle of 10–16°. Two imaging prisms in the optical path ensure that the image is upright and aligned with the real object. Most of the ordinary stereo microscopes used in routine use the Greenough principle.
Key technical parameters:
| Eyepiece | Standard configuration: 10X/22mm, large field of view, wide angle, high eye point, providing convenience for observers wearing glasses, 15X 20X 30X eyepiece is also optional |
| Observation head | 45° tilt, 360° rotation, interpupillary distance adjustment range 54-75mm: bilateral diopter adjustment ±5 |
| Objective lens | Standard configuration: 0.67X-4.5X continuous zoom objective lens, zoom ratio 6.7:1, to ensure that the image plane is parfocal at each magnification, binocular imaging is easy to overlap, and the imaging stereoscopic effect is strong |
| Focus bracket | Vertical arm focusing bracket, the hand wheel is adjustable, and the lifting range is 106mm |
| Base | Vertical arm LED lighting base, large glass plate with a diameter of 180mm. |
| Lighting | Up and down transflective LED lighting, independent switch brightness adjustable |
Imaging renderings:

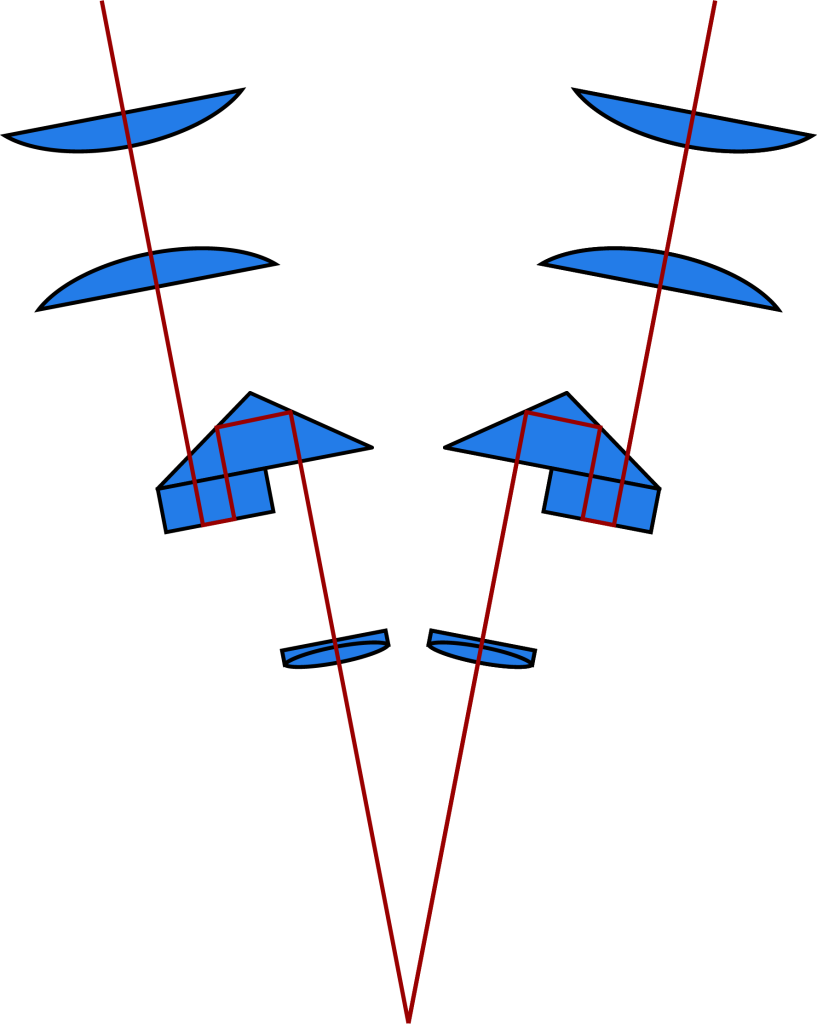
Galileo’s light path diagram is as follows:
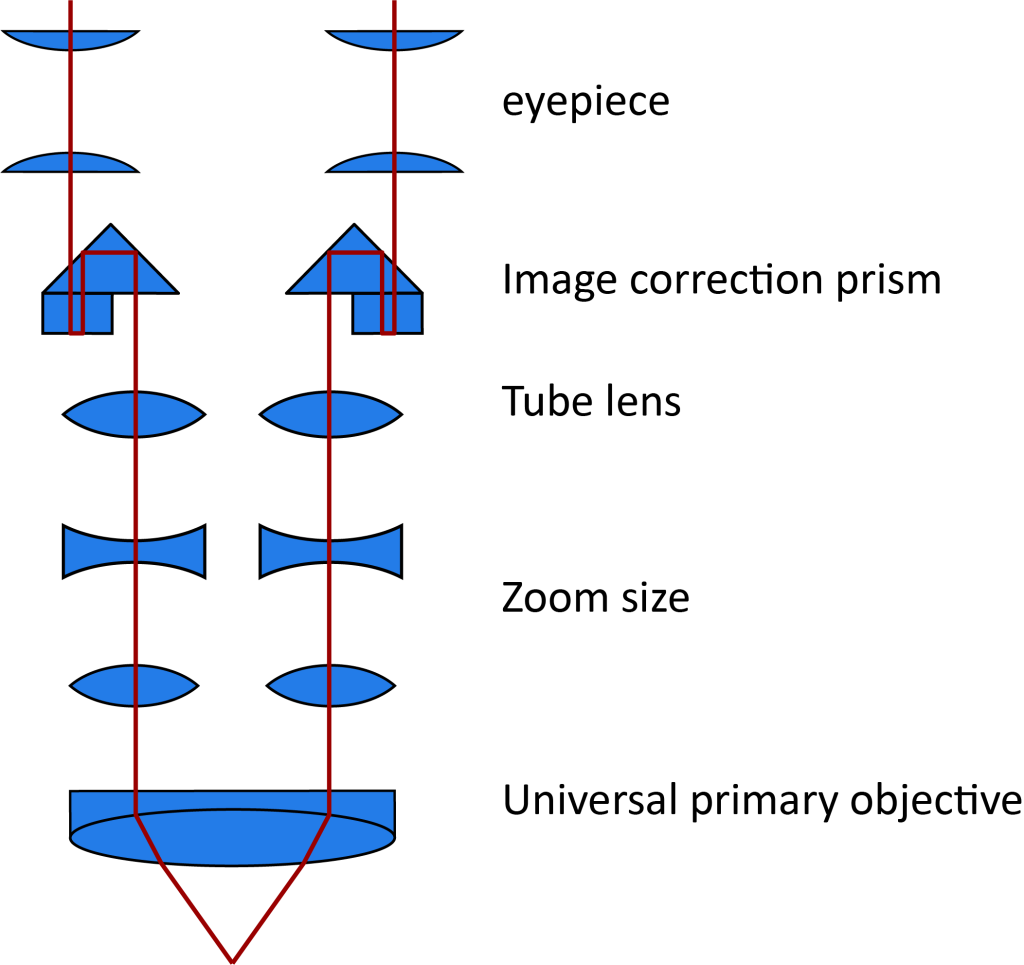
Galilean Optical Path Principle: The optical system consists of two parallel beam paths and a shared main objective, which is why it is called a CMO (Common Main Objective) system. This type of stereo microscope has a movable observation tube and universal accessories that can be customized in the tube scope area. The stereofluorescence accessory is an important optical accessory. The stereo microscope of the Galileo optical path can be upgraded to a stereo fluorescence microscope by adding the upper stereo fluorescence accessory, and has become one of the important tools in the fields of modern life science, regenerative medicine, and genetics.
Key technical parameters:
| Accessories | Parameters |
| Observation tube | Tilt angle 30°, 2 gears optional (binocular 100%; trinocular 80% – binocular 20%) adjustment range: 55 -75mm |
| Eyepiece | 10X/22mm, diopter adjustable +/-5 (standard configuration) |
| Objective lens | 8X-56X, zoom ratio: 7:1, apochromatic objective lens PLAPO 1X, W/D 81mm |
| Base | Mirror body transflective LED lighting, ring LED lighting, optional high-contrast special base |
| Fluorescence accessory host | Dual optical path fluorescence integrated modular design, patented product, one-key switching of fluorescence channels, fast response. changeDisc-type 4-channel 8-hole fluorescent lighting, accurate positioning. High-power LED fluorescent light source, long service life, no need to replace the bulb. There are many options for fluorescent channels.UV excitation group: 350/50nm 400nm 420nmLPBlue excitation group: 470/40nm 500nm 530/50nmGreen excitation group: 530/40nm 565nm 575nmLP |
3. Application of Stereo Microscope
- 1. Studies in zoology, botany, entomology, histology, mineralogy, archaeology, geology and dermatology, etc.
- 2. In the textile industry, it is used for the inspection of raw materials and cotton wool fabrics.
- 3. In the electronics industry, it is used as an operation tool for spot welding and inspection of transistors.
- 4. Inspection of surface phenomena such as crack formation and pore shape corrosion of various materials.
- 5. Devices for machine tools, observation of work processes, inspection of precision parts, and assembly tools when manufacturing small precision parts.
- 6. Surface quality of lenses, prisms or other transparent substances, and quality inspection of precision scales.
- 7. Distinguishing the authenticity of documents and coins, and retrieving evidence for criminal investigations.
- 8. Widely used in textile products, chemical engineering, plastic products, electronics manufacturing, machinery manufacturing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing, printing industry, colleges and universities, archaeological research and many other fields.